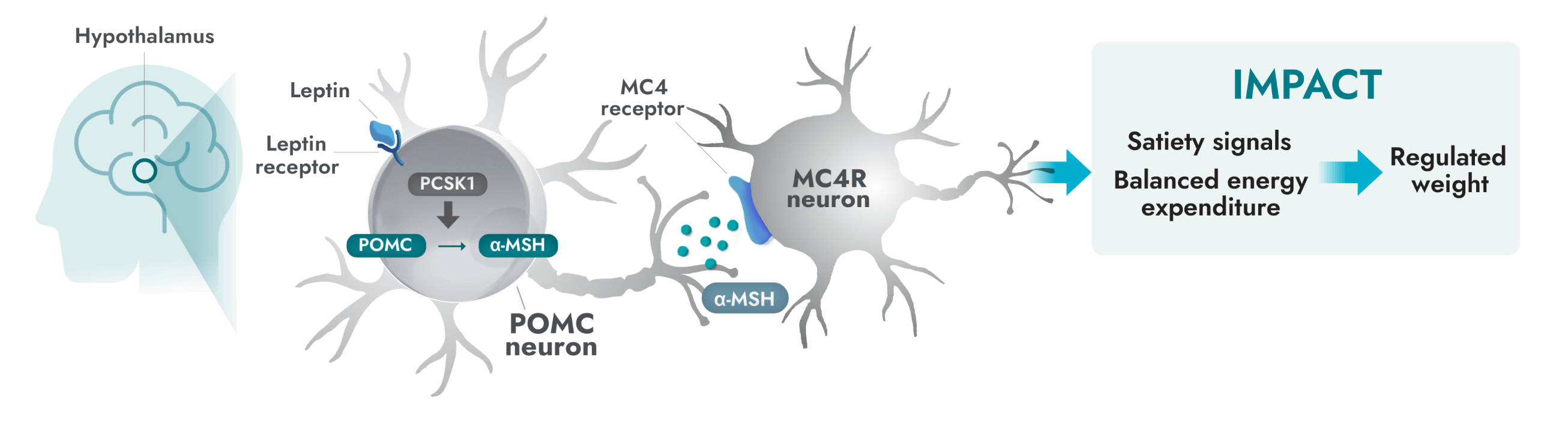
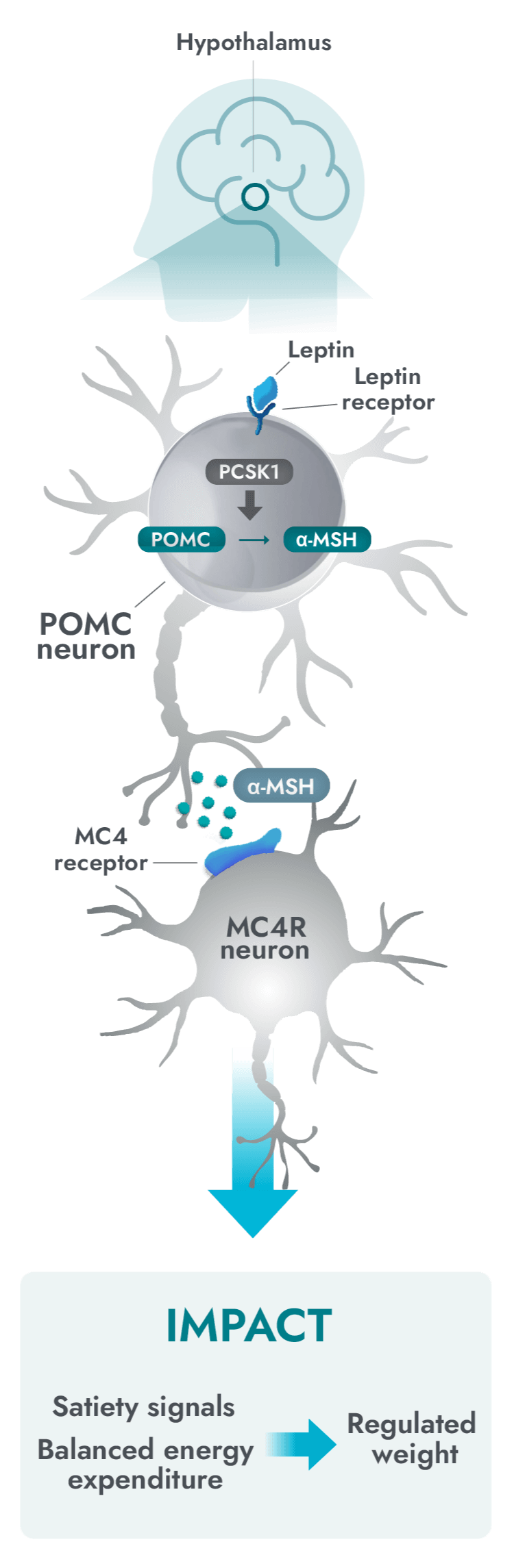
The MC4R pathway in the hypothalamus is a key neuronal pathway in regulating hunger, caloric intake, and energy expenditure1
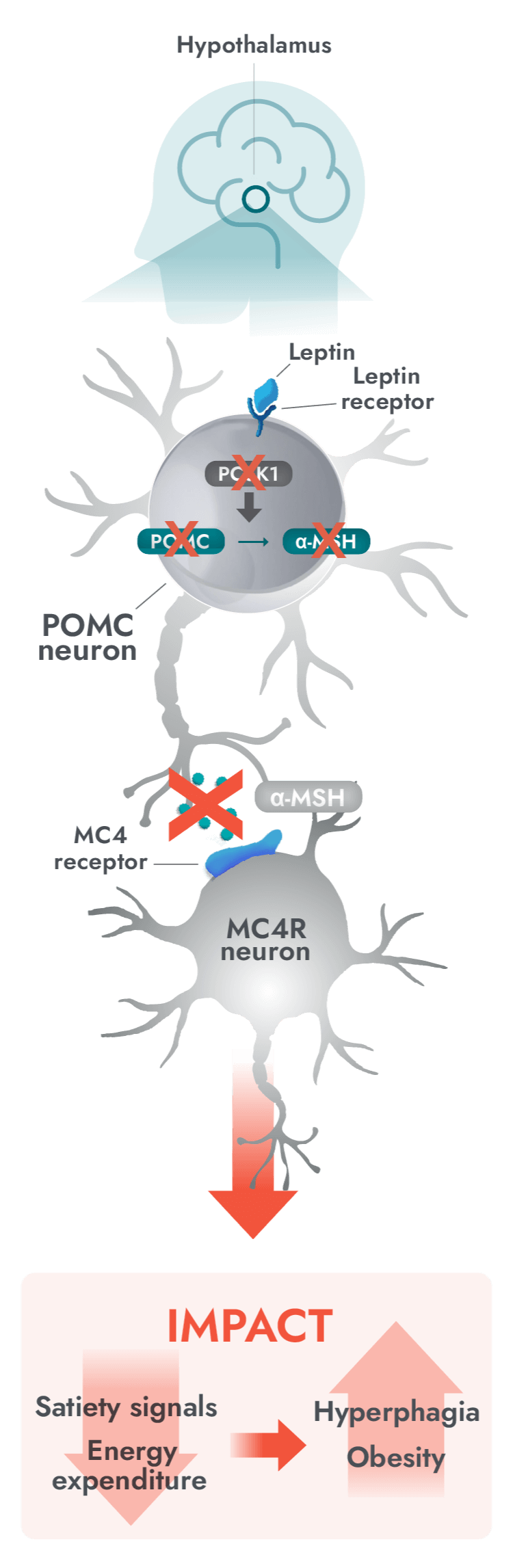
Impairment in the MC4R pathway is a root cause of hyperphagia and obesity in POMC, PCSK1, and LEPR deficiency1
- In people with POMC, PCSK1, or LEPR deficiency, genetic variants can disrupt signaling.
- Alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) production is impaired or deficient, preventing activation of the MC4 receptor, therefore impairing regulation of energy expenditure and satiety signaling.

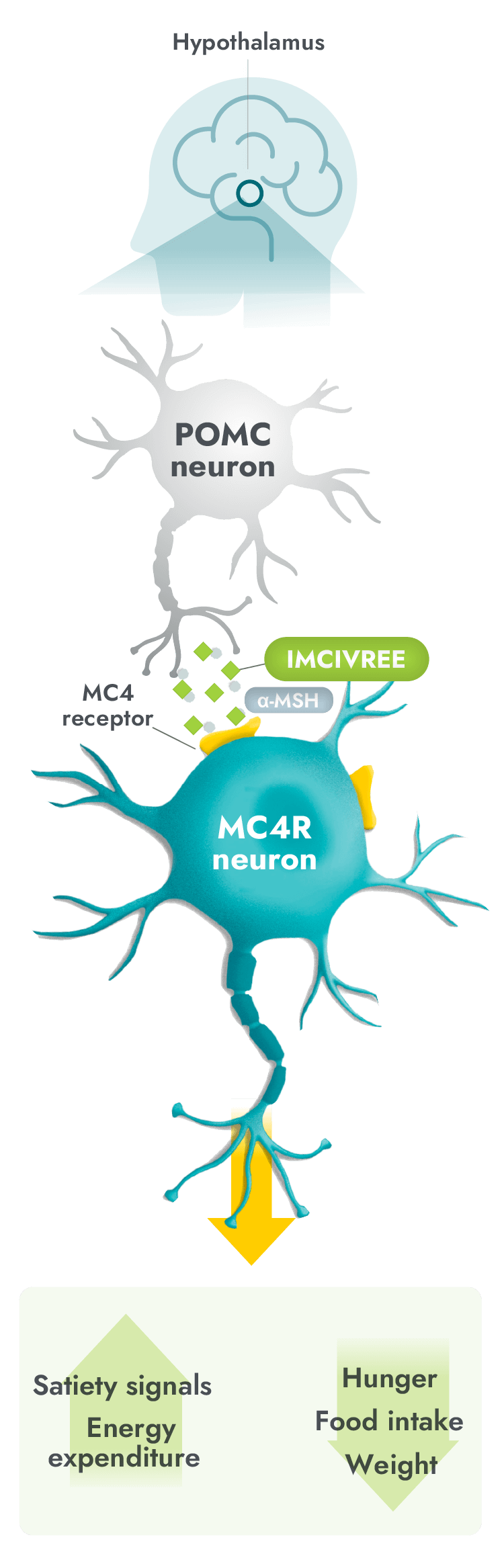
IMCIVREE is the first and only precision medicine to target impairment in the hypothalamic MC4R pathway3,4
- IMCIVREE, an MC4R agonist, acts in place of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) to activate the MC4 receptor, to reestablish MC4R pathway activity.3,5,6
-
- Activation of the MC4R pathway can help to increase satiety signals and energy expenditure, therefore reducing hunger, and consequently, food intake and weight.3
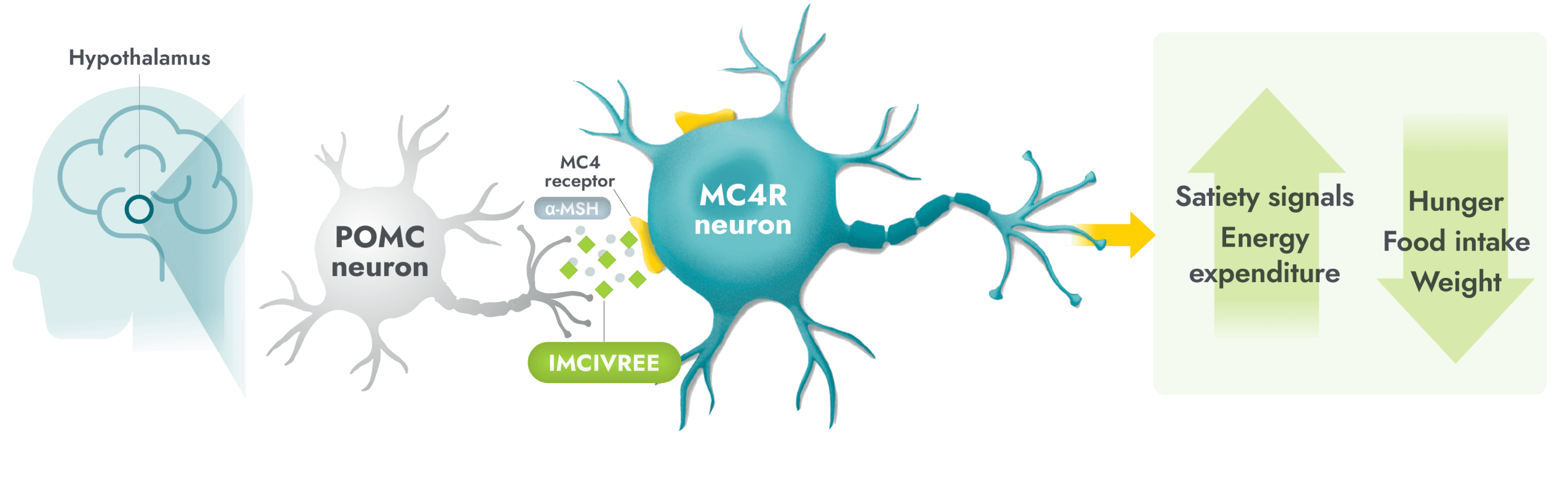
LEPR=leptin receptor; MC4R=melanocortin-4 receptor; PCSK1=proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1; POMC=proopiomelanocortin.
References: 1. Eneli I, Xu J, Webster M, et al. Tracing the effect of the melanocortin-4 receptor pathway in obesity: study design and methodology of the TEMPO registry. Appl Clin Genet. 2019;12:87-93 doi:102147/TACGS199092. 2. Huvenne H, Dubern B, Clément K, Poitou C. Rare genetic forms of obesity: Clinical approach and current treatments in 2016. Obes Facts. 2016;9(3):158-173 doi:101159/000445061. 3. IMCIVREE [prescribing information]. Boston, MA. Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 4. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved drug products with therapeutic equivalence evaluations (the orange book). 44th ed (2024). 5. Trapp CM, Censani M. Setmelanotide: a promising advancement for pediatric patients with rare forms of genetic obesity. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2023;30(2):136-140 doi:101097/MED0000000000000798. 6. Haws R, Brady S, Davis E, et al. Effect of setmelanotide, a melanocortin-4 receptor agonist, on obesity in Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22(11):2133-2140 doi:101111/dom14133.